How to conduct qualitative research: a step-by-step guide and examples
Conduct qualitative research to understand customer behaviour and make informed decisions.

Qualitative research is the first step towards fulfilling your customers’ needs, increasing customer satisfaction and driving brand loyalty.
How? Qualitative research explores the “why” behind customer actions, preferences and emotions. Like a good conversation, you can dig into customer reasoning, uncovering valuable information that isn’t available through quantitative research alone.
Our guide will walk you through conducting your own qualitative research in six easy steps to get to the heart of what your customers want.
What is qualitative research and why is it important?
Qualitative research is descriptive data used to investigate people’s opinions and motivations, providing valuable insight into their behaviour. The data collected in qualitative studies explains why people feel the way they do and is helpful for brand tracking, event planning and product development.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which collects and analyses data that can be measured numerically. It complements quantitative research by providing deeper insights than numbers alone can offer. You can also think of it as hard versus soft or social sciences.
Qualitative research can be conducted as a standalone study or used in a mixed-method study that gathers qualitative and quantitative data. Typically, qualitative research relies on interviews, focus groups and observation, as well as surveys with open-ended questions inviting written responses which provide deeper insights.
How to conduct qualitative research in 6 steps
Although your qualitative research methodology needs to be uniquely suited to your goals, there are a few standardised steps involved in the process. These steps serve as guidelines to develop your unique approach.
1. Identify your question, problem or goal
To define a clear research objective, consider SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound) goal-setting and what it is you want to accomplish in the study.
Perhaps you want to conduct primary research to answer specific business questions. Alternatively, perhaps you’re conducting exploratory research in order to understand an issue better. The clearer you are about what you want to accomplish, the more able you will be to follow the rest of the steps outlined here.
Some examples of qualitative research questions are:
- Which factors have the biggest impact on consumers when deciding which brand to shop?
- How do customers feel about our product quality?
- How can our brand effectively stand out during our next product launch?
- What motivates customers to choose our brand instead of one of our competitors’ brands?
- What emotions do people feel when purchasing our products?
Related: Setting a goal for your survey
2. Make your hypothesis
A hypothesis is a statement that guides a qualitative research study. It uses your research goal to form an expectation about what the data will reveal. Researchers form a hypothesis as a north star to help them stay on track.
For example, let’s suppose that a product marketer wanted to understand the biggest factors affecting whether or not a consumer purchases their new product. To form a hypothesis, the researcher would consider the goal of the study and make a tentative statement.
In this example, the hypothesis might be the following: “Product packaging and branding are the two biggest draws to our new product.”
Let’s use craft beer market researchers for our second example. Craft beer market researchers might form the following hypothesis: "Millennial craft beer consumers prefer beer with unique flavour profiles, such as fruit-infused or sour varieties, due to their desire for novelty and differentiation.”
This hypothesis could guide exploration, such as focus groups with millennials exploring their flavour preferences or surveys investigating why people choose specific craft beers.
3. Create a qualitative research plan
The next step is to create a qualitative research plan to structure your market research study. Researchers can effectively address their hypothesis with effective research design. There are several types of research design to consider for your qualitative research plan.
Here’s a brief explanation of the various research design types:
- Exploratory research design: This design type aims to unearth insights from participants who are familiar with your research subject.
- Descriptive research design: This design type focuses on the current characteristics of a research subject by gathering feedback from participants who are familiar with the subject.
- Correlational research design: This design type looks for relationships between variables in a study to make predictions.
- Experimental research design: This design type aims to understand a cause-and-effect relationship between two variables. In this method, a researcher changes an independent variable to assess its effect on a dependent variable.
In addition to research design, you must consider the type of research. Typically, researchers use one of four different approaches in qualitative data collection. Before brainstorming effective research questions, you must decide on the best method.
4. Choosing the right qualitative research method
Several qualitative research methods have distinct benefits that can support your research goals. Here, we cover seven qualitative research methods that you could choose from.
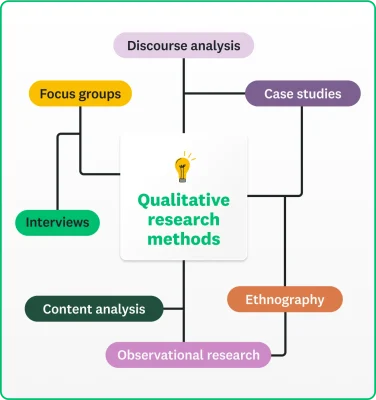
Interviews
What they are: Interviews are a traditional qualitative research method frequently used in market research and polling. In an interview, a qualitative researcher has a one-to-one conversation with a consumer.
Benefits:
- Interviews allow researchers to ask follow-up questions in real time.
- They enable researchers to observe body language and non-verbal cues.
When to use: Use interviews to explore consumers’ personal experiences, motivations or emotions.
Focus groups
What they are: Focus groups are conducted with a small group of people who are selected based on specific demographics. A trained facilitator guides a conversation to collect in-depth information about consumer opinions.
Benefits:
- Focus groups enable researchers to observe open discussions about a product, service or idea.
- They allow for new topic areas to emerge from conversations.
When to use: Use focus groups to understand the nuances of a topic and get consumers’ first impressions of a new product or idea.
Ethnography
What it is: Ethnography is a form of qualitative research whereby researchers immerse themselves deeply in the natural setting of a specific group or community. The qualitative researcher observes people’s behaviours to understand the group’s motivations and beliefs.
Benefits:
- Ethnography allows researchers to make first-hand observations in natural environments.
- It enables researchers to observe spontaneous dynamics and behaviours that aren’t detected in interviews or focus groups.
When to use: The primary use of ethnography is to understand the nuances of a culture by observing daily life.
Case studies
What are they: Case studies are used to analyse a specific group, person or situation in order to prove a predetermined hypothesis or principle. Researchers examine a subject critically to recommend a solution.
Benefits: Case studies strengthen a company’s value proposition in marketing.
When to use: They are often used to solve problems, identify important relationships and develop hypotheses. Case studies are also used in marketing to demonstrate the effectiveness of a product or service.
Observational research
What it is: Observational research involves observing consumers in their natural environment.
Benefits:
- Observational research enables researchers to see how consumers behave in their most natural state.
- It helps researchers to identify how consumers behave when no one is watching.
When to use: Use observational research to observe behaviours that might not be easily recalled in an interview. For example, researchers may observe how long consumers take to decide on a product when shopping in their store.
Content analysis
What it is: In content analysis, a researcher evaluates qualitative data, such as text, videos and images, to identify patterns or themes. The researcher counts the occurrence of certain words, phrases or concepts within the qualitative data.
Benefits: Content analysis is a lower-cost research method than the likes of focus groups.
When to use: Researchers use content analysis to understand the underlying messages or themes by quantifying the presence of specific elements.
Discourse analysis
What it is: In discourse analysis, a researcher analyses conversations to examine how language is used in different social contexts. Researchers analyse conversations, interviews and documents to see how language forms social identities and affects actions.
Benefits: Discourse analysis helps you analyse text and conversations in their context.
When to use: Discourse analysis is particularly useful in terms of understanding different power dynamics, cultures and societal norms for specific demographics.
Sometimes, researchers don’t want to conduct qualitative research alone. They may want to support their efforts with different types of quantitative research to get a broader perspective. Combining qualitative and quantitative methods can help you make detailed descriptions with statistical analysis that backs it up.
5. Conduct qualitative research
Once you’ve determined what you want to do, the hypothesis that you want to test and how you will do that, it’s time to do the research. To gather qualitative data effectively, make sure that you choose the best data collection method for your specific objectives.
Surveys
After considering your research method options, you might choose to survey your target audience. Online surveys are the most cost-effective survey types as they can be sent via email, embedded in websites or shared on social media. When creating questions for qualitative surveys, focus on open-ended questions that allow respondents to answer freely. Don’t limit responses to predefined options.
SurveyMonkey streamlines the data collection process to help you quickly gather and analyse qualitative data.
“With SurveyMonkey, we can easily look at trends and graph that information,” says Bill Wilson Center Division Director Laura Foster.
“I really appreciate all the different ways that I can filter results and look at the aggregate data. And we’re always asking open-ended questions to get open feedback from people; SurveyMonkey makes it easy to identify themes within that qualitative data.”
Interviews or focus groups
If conducting interviews or focus groups, write down open-ended questions that encourage participants to share descriptive insights. If you opt for observational research, prepare criteria for your observations in order to ensure consistency.
Next, you will need to recruit participants who reflect your research objectives. When choosing participants, ensure that you gain their informed consent by explaining to them the purpose of the research and how the data will be used.
If conducting interviews or focus groups, it is all the more important to create a comfortable environment for participants. You should also assure participants there are no right answers and that they should reply candidly.
The beauty of qualitative research is that it provides researchers with significant flexibility. While using a set of predefined questions for participants, stay open to exploring any topics that may crop up in conversation. If using surveys as your qualitative research method, you should monitor responses to ensure completeness and follow up with respondents if clarification is needed.
6. Analyse and report on the results
Once you’ve collected your qualitative data, you’ll need to analyse it to find out whether it supports your hypothesis. Immerse yourself in the data by reading transcripts or field notes, reviewing survey responses or listening to recordings. When you’re familiar with the data that is available, you should highlight observations in your datasets for further investigation. You should also document your analysis for subsequent reporting.
Coding, or categorising emerging trends in a dataset, is one popular qualitative data analysis technique. In coding, you organise the unstructured data using labels for recurring ideas, words, phrases or themes, etc. By separating the data into meaningful categories, you can gain valuable insights.
You can also determine overarching insights about a sample by grouping together similar responses. This is called thematic analysis, which researchers use to identify, interpret and understand participant perspectives.
Bear in mind the fact that thematic analysis is an iterative process. As you engage in qualitative data analysis, you might see specific themes emerging over and over again. Once you’ve identified those themes as relevant and meaningful, you might restart the analysis process and review the data again, looking for fresh insights into those themes.
Finally, you’ll need to summarise your findings and connect them to your hypothesis. When presenting your findings, remember to:
- Make your report visual: Consider visualising your data with a word cloud or using impactful quotes from your qualitative research to tell a story. Highlight adjectives from your sentiment analysis to show how respondents feel.
- Provide specific recommendations: It’s helpful to provide specific recommendations based on your research findings.
- Avoid jargon: Make sure you use language that all stakeholders can understand. Explain technical terms to your audience to ensure clarity.
Use these six simple steps to conduct qualitative research and gain a better understanding of your target market.
Types of qualitative research
There are four main types of qualitative research that are commonly used for consumer research. Each qualitative research type offers different benefits for researchers. Let’s review the types to determine the most relevant one(s) for your research.
Phenomenological research
This form of qualitative research aims to understand the shared essence of a phenomenon or human experience. In simpler terms, phenomenological research studies universal lived experiences to understand how a group thinks. Researchers want to uncover what an experience means to a group of people.
Phenomenological research asks: “What is it like to experience ______?” It is used to understand diverse viewpoints.
Grounded theory
In grounded theory, a researcher collects data and analyses it to develop theories from patterns that emerge. This form of research uses an inductive approach where theories arise from collected data, rather than the other way around. It is an iterative process where analysis and data collection occur in tandem.
Researchers use grounded theory to uncover social processes or the dynamics and behaviours of a group.
Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research explores the natural behaviours, culture and traditions of a group of people. It takes observational research one step further by requiring the researcher to live among the subjects in their natural setting. In ethnographic research, researchers can gather in-depth insights by experiencing people’s everyday lives first-hand.
Ethnographic research helps researchers to gain an in-depth understanding of people’s attitudes and behaviours.
Historical research
Historical research uses primary sources such as documents, letters and diaries to study past events. Researchers gather information from these primary sources and interpret it using historical context to understand current events. This form of research helps research teams to make predictions about future events. In historical research, teams analyse data to identify common themes and patterns.
Historical research digs into old data to understand important events, people and cultures from the past.
These are the four main types of qualitative research. However, there are also other options, including narrative research. Finding the appropriate research method will ensure that your findings align with your market research goals.
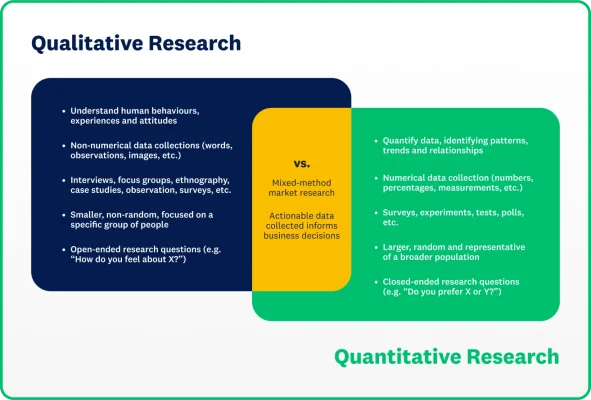
Qualitative vs. quantitative research
Qualitative research is designed to give researchers a clear understanding of the unique perspectives, opinions, behaviours and experiences of a certain group. It is unquantifiable and focuses on gathering descriptive feedback from subjects through interviews, focus groups and surveys, etc.
The qualitative research method garners primary research data. However, before you compile your final report, consider adding secondary research as well. Integrating your original research data with existing qualitative methods can deepen the story that your results tell.
Quantitative research is numerically measurable and uses closed-ended questions to gather data from a sample group. Quantitative research methods test hypotheses about a sample population. Numerical data is collected through surveys with closed-ended questions, experiments, polls and tests.
| Qualitative research | Quantitative research | |
| Purpose | To understand human behaviours, experiences and attitudes | To quantify data, identifying patterns, trends and relationships |
| Data type | Non-numerical (words, observations, images, etc.) | Numerical (numbers, percentages, measurements, etc.) |
| Data collection methods | Interviews, focus groups, ethnography, case studies, observation, surveys, etc. | Surveys, experiments, tests, polls, etc. |
| Sample Size | Smaller, non-random, focused on a specific group of people | Larger, random and representative of a broader population |
| Research questions | Open-ended (e.g. “How do you feel about X?”) | Closed-ended (e.g. “Do you prefer X or Y?”) |
Advantages and disadvantages of qualitative research
Are you wondering about the pros and cons of choosing qualitative research methods for your study? If so, there are two sides to every coin, and we will look at the positive and negative aspects of this type of research.
Pros
- In-depth understanding: Qualitative research provides a deeper understanding of why consumers behave in certain ways. It allows you to gather descriptive feedback about people’s opinions, feelings and experiences.
- Contextual insights: With qualitative research, you can gain a better understanding of the context in which consumer behaviours develop.
- Participant-centred: You can gather feedback from a diverse range of subjects to gain new perspectives. Qualitative research can lead to more authentic data because participants can express feelings in their own words.
- Explore complex issues: Qualitative research is ideal for exploring topics requiring a nuanced understanding. It enables teams to dive deeper than numerical data alone.
- Cultural sensitivity: This form of research is also great for understanding social nuances when studying different groups or cultures.
Cons
- Time-consuming: Qualitative research often takes more time to conduct and analyse than quantitative research. It involves analysing individual responses or spending time immersed in a sample group.
- Resource intensive: This form of research is also resource intensive and may require you to use trained interviewers or transcription services.
- Potential for misinterpretation: When collecting qualitative feedback, there is a greater potential for misinterpretation. Open-ended responses are less concrete than quantitative data, so you must take a more refined approach.
- Difficult to generalise: Unlike quantitative data, with qualitative data it is more difficult to make generalisations about a certain population. Qualitative research typically focuses on small samples that might not accurately represent a larger population.
As with any form of research, you must evaluate your goals and determine whether qualitative research methods will meet your needs. Although it may present some challenges, qualitative research is a highly effective method of learning about consumer behaviour.
Streamline your qualitative research with SurveyMonkey
By following the qualitative research steps in this article, you will gain the data you need to develop a product, plan an event or improve your customer experience. Remember to clarify your objectives, form a hypothesis, choose the best method for your needs, analyse the data and report your findings.
When it comes to qualitative research, surveys remain a powerful way to collect valuable feedback at scale. SurveyMonkey enables a seamless qualitative research process to give you the usage and attitudes insights that you need.
Are you ready to conduct your own research? If so, choose from hundreds of expert-written survey templates and open-ended questions that are designed to give you reliable results. Create online forms to start collecting consumer feedback today.
Ready to get started?
Discover more resources

Solutions for your role
SurveyMonkey can help you do your job better. Discover how to make a bigger impact with winning strategies, products, experiences and more.

How to Write a Research Question
Discover how to write a research question that drives meaningful insights. Follow this step-by-step guide to create impactful questions.

The Importance of Market Research for Your Business
Market research helps you to understand customers, spot trends and reduce risks. Discover 10 key benefits and how to leverage insights for growth.

Hornblower enhances global customer experiences
Discover how Hornblower uses SurveyMonkey and powerful AI to make the most of NPS data, collect customer insights and improve customer experiences.