Sample size calculator
Use our accurate sample size calculation tool and learn how sample size works. Looking for more? Explore features and survey templates designed to get you reliable results.

Calculate your sample size
Population Size
Confidence Level (%)
Margin of Error (%)
Sample size
383
Doing market research? SurveyMonkey Audience finds you the right survey respondents quickly and easily and helps you target them according to demographics, consumer behaviour, geography or even designated marketing area.
How many people do you need to take your survey? Our sample size calculator makes collecting the correct number of responses easy.
What is sample size?
Sample size is the number of completed responses your survey receives. It should represent the target population whose opinions or behaviour you care about.
Let’s explore:
- The different ways to interpret your sample’s results
- The formula used to calculate sample size
- Why having an appropriate sample size for a survey matters
- How the significance of sample size varies across survey types
- Sample size best practices to use when calculating your sample size
Data you need for sample size calculation
Here are the key terms that you’ll need to understand in order to calculate your sample size:
Population size represents the total number of people in the group you are trying to study. If you were surveying people in the United Kingdom, the population size would be just over 68 million. When surveying your company, your population size will be the total number of employees.
The margin of error is a percentage that shows how accurately survey results reflect the opinions of the whole population. The lower the margin of error, the more accurate the answer is at a given confidence level.
Confidence level measures how sure you can be that the population will choose an answer within a certain range. For example, a 95% confidence level means you can be 95% certain that the results lie between x and y numbers.
Confidence interval: The confidence interval represents a statistical range that indicates where the true result probably is. For example, a 95% confidence interval indicates that if you sampled the same population numerous times, your true result would lie within the interval in approximately 95% of the samples.
How to calculate sample size
How do you determine the minimum sample size for your survey? If you’d like to do the calculation by hand, use the following formula:
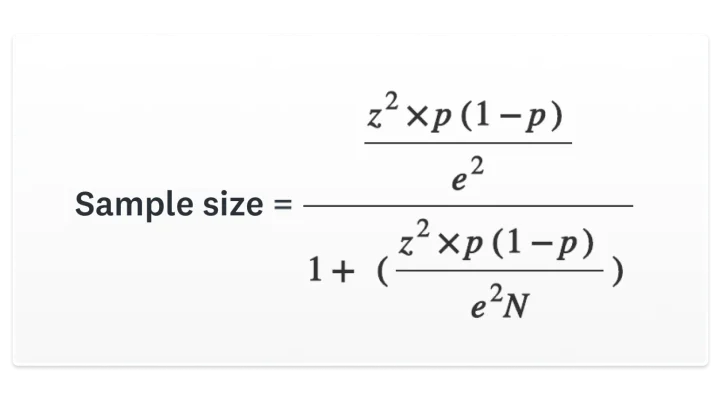
N = population size • e = Margin of error (percentage in decimal form) • z = z-score
The z-score is the number of standard deviations a given proportion is away from the mean. To find the right z-score to use, refer to the table below:
| Desired confidence level | z-score |
| 80% | 1.28 |
| 85% | 1.44 |
| 90% | 1.65 |
| 95% | 1.96 |
| 99% | 2.58 |
Real-world sample size calculation examples
Let’s work through some sample size examples:
Example 1: Surveying delivery workers
Let’s suppose you’d like to survey delivery workers in a city with a population of 500,000. You want your sample size to have a 95% confidence level and a margin of error of 5%. Using the formula (or calculator above), you can calculate your sample size as 384.
Example 2: Company-wide survey
In contrast, if you conducted a company-wide survey with 300 employees and wanted an 80% confidence level and a 10% margin of error, your sample size would be 37.
Things to watch out for when calculating sample size
- If you want a smaller margin of error, you must have a larger sample size given the same population.
- The higher the sampling confidence level you want, the larger your sample size will need to be.
What is a good sample size?
Your survey sample size will often depend on your study’s objective and the population you’re surveying.
For example, you may only need to include some customers when using a customer feedback survey. On the other hand, political pollsters must carefully select a balanced sample size to reflect the overall population accurately.
Here’s how each value can affect your survey:
The effect survey values have on the accuracy of its results
| Value increased | Value decreased | |
| Population size | Accuracy decreases | Accuracy increases |
| Sample Size | Accuracy increases | Accuracy decreases |
| Confidence level | Accuracy increases | Accuracy decreases |
| Margin of Error | Accuracy decreases | Accuracy increases |
Sample size determination by survey type
Specific use cases can help you determine whether to use a statistically significant sample size:
- Employee and human resources surveys offer vital insights into employee sentiments. While a statistically significant sample size provides a broader view, smaller samples are valuable for identifying areas for improvement in a workplace.
- Customer satisfaction surveys don’t always require a large sample size. Accuracy and representing customer sentiments are essential, but examining each response closely is crucial to the business. Every piece of feedback, whether positive or negative, is important.
- Market research surveys require a large enough sample size for you to gain important insights about your customers and target market. It ensures that you effectively gather accurate information that represents your target market.
- Education surveys should have a statistically significant sample size to ensure meaningful insights. However, a statistically significant sample size might be less important if the goal is simply to gather student feedback.
- Healthcare surveys require a statistically significant sample size to identify patient concerns and advance medical research. The necessity for such a size is lower for patient satisfaction or routine care assessments.
- Casual surveys are informal surveys that you can send to friends, colleagues or family. These fun surveys don’t typically require a statistically significant sample size.
What’s a large sample size?
There isn’t a universal standard for determining a large sample size. Your sample size will often vary depending on the context, such as the field of study or the research goal.
A large sample size typically provides enough statistical power to detect meaningful differences in your studied population. In many fields, experts consider a sample size of several hundred or more to be large.
However, researchers decide how many samples to use based on factors such as statistical power or available resources. Your sample size may also depend on the type of analysis you’re conducting. Some statistical tests may require larger sample sizes than others.
Additionally, it’s worth considering that the population’s complexity may determine how large your sample size is. A larger sample size may be necessary for highly diverse populations or when studying rare phenomena.

Sample size best practices
Use these tips to calculate the best sample size for your survey:
Determine what to use your data for
The purpose of your data may determine your sample size. If your sample size is too small, then the results of the survey may not be accurate. If it is too large, then the survey may prove to be expensive or require more time to complete.
When collecting survey data, you may need a bigger sample size to obtain accurate results or apply findings to a larger group. Smaller samples could be enough if you use the sample survey data primarily for qualitative insights.
Work within your budget and time limits
Larger samples may be more costly due to data collection expenses, participant incentives and analysis. With a smaller budget, you may opt for a smaller sample size. Time constraints may also influence sample sizes.
If you don’t have much time for the survey, use a smaller sample size to gather accurate data quickly. If time allows, aim for a larger sample size to increase the precision of your results.
Consider survey type
Different survey types may require different approaches to sample size determination. Customer feedback surveys are helpful with smaller sample sizes. Political polls, on the other hand, require larger and more representative samples. Tailor your approach to ensure that the results are statistically sound and reliable.
Use open-ended survey questions
Open-ended questions ask for detailed answers, making surveys take longer to finish because respondents need to write more. As a result, some respondents may not finish your survey, making it harder to achieve a large sample size. Adjust the number of open-ended questions or plan your sample size accordingly.
Common sample size mistakes to avoid
Failing to address common sample size mistakes may undermine the effectiveness of your survey. When calculating your survey’s sample size, avoid these potential pitfalls:
- Overlooking margin of error: The margin of error indicates the level of precision and reliability in the survey results. Neglecting to consider the margin of error may result in an insufficient sample size, leading to less reliable conclusions.
- Inadequate confidence level: The confidence level represents the level of certainty in the estimated outcome. Failing to set an adequate confidence level may impact the precision of the survey results.
- Incompatible survey type: Different survey types require specific sample sizes based on the desired level of accuracy and precision.
- Relying on small sample size: Using a small sample size without considering statistical power may lead to biased and non-representative results.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
- What is sample size?
- What do I need in order to calculate my survey sample size?
- How do I calculate my survey sample size?
- What is a large survey sample size?
Get more survey responses faster
Use our sample size calculator for better survey results. If you need more respondents, use SurveyMonkey Audience to find survey participants globally and collect responses from almost anyone.
Discover more resources

Insights Manager
Insights managers can use this toolkit to help them deliver compelling, actionable insights to support stakeholders and reach the right audiences.

Continuing healthcare checklist: what UK healthcare providers need
Learn what information healthcare and social workers need to provide for a continuing healthcare checklist, what happens next and possible outcomes.

Turning employee engagement statistics into actionable surveys
Discover how to use UK employee engagement statistics to design effective surveys. Use actionable insights to boost retention and drive productivity.

Shaping the future: how British values in the workplace drive inclusion and engagement
Discover how ‘British values in the workplace’ surveys can reveal what matters most to employees, fostering inclusion and engagement.
Need more survey responses?
Tap into SurveyMonkey Audience, our global survey panel of real people ready to tell you what they think.